P8. Variables
A variable stores data that can be changed later on. Project with Flow support can have both global and local variables. Global variables are visible from all Flows, local variables are visible only inside the Flow in which it is defined.
Project without Flow support can have only global variables and those variables must be Native i.e. variables managed by the native code (written in C++).
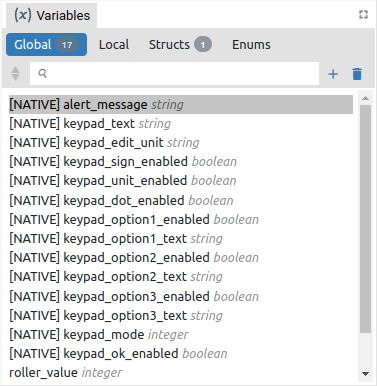
To add variables, use the Variables panel (Fig. 1), when a dialog box will open for defining the basic parameters of the variable (Name, Type and Default value).
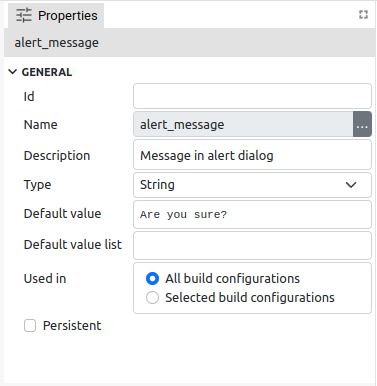
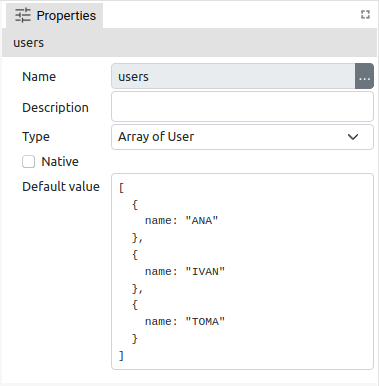
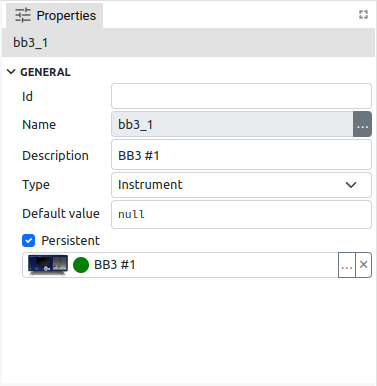
To edit the parameters of the variable selected in the Variables panel, use the Properties panel. In Fig. 2, Fig. 3 and Fig. 4 shows Properties panels for different types of variables from different types of projects.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item |
Description |
|
Id |
ID is EEZ-GUI project specific and is used in Page, Action, Global Variable, Style, Font, Bitmap and Colors. These are all resources that are referenced by name in the project editor. When that project is built, names are no longer used, but numerical IDs. This field is optional, i.e. an ID does not have to be specified, in which case an ID will be assigned during the build. However, if we want an object to always get the same ID, then it needs to be defined. Why would we want to always have the same ID? This is necessary when there is a master project such as modular-psu-firmware.eez-project from EEZ BB3 and that master project is used by BB3 Applets and BB3 MicroPython scripts and they can use resources from the master project that have that ID defined.
Important: once the ID is set, it should not be changed, otherwise all BB3 scripts that depend on it should be rebuilt. |
|
Name |
Variable is referenced in other parts of project by its name. Rules for naming variables: Starts with a letter or an underscore (_), followed by zero or more letters, digits, or underscores. Spaces are not allowed. |
|
Description |
Optional field, contains a description of the variable. |
|
Type |
The type of data stored in variable. When adding a new variable, its suggested default value will depend on the selected type (0 for Integer, False for Boolean, etc.). |
|
Native |
The variable is managed by the native code (written in C++). A Dashboard project cannot have Native variables, and working with them is explained in Chapter XX. |
|
Default value |
Default value is the initial value of the variable when Flow starts. Given in JSON notation (https://www.json.org/json-en.html).
For example: 123, "Hello", true If types is struct: { "member1": 42, "member2": "Hello" } If type is array: [1, 2, 3] or ["string1", "string2", "string3"] |
|
Default value list |
Only supported in EEZ-GUI project that does not have EEZ Flow enabled. |
|
Used in |
See Configurations in project Settings. |
|
Persistent (Global variables only) |
Stores the last value of the variable in the .eez-runtime-settings file, so that next time projects will have this value, instead of the default value.
Supported only in Dashboard projects. |
P8.1. Variables usage in the project with EEZ Flow enabled
Data stored in a variable can be accessed using expressions. The following Action components are used to work with variables:
- Evaluate – evaluates expression, which can use variables, and sends the result through "result" data line.
- Watch – monitors the change in the value of the variable. At Flow start, it always sends the current value via the Changed data flow line, and later every value change is sent.
- SetVariable – sets a new variable value. Multiple entries are allowed. Each entry contains a variable and an expression field. During Flow execution, the evaluated expression will be stored in a variable.
- SwitchCase, Compare, IsTrue – Actions used for branching in the Flow depending on the value of the variable
Variables are also used in Widget components. Certain Widget properties can be defined as an expression. In this case, the value of that property will change during Flow execution as the expression changes. For example, Label widget can show the content of some variable, and it will updated every time this variable has been modified.
P8.2. Variable types
P8.2.1. Basic/Primitive types
|
Item |
Description |
|
Integer |
Signed 32-bit integer. |
|
Float |
IEEE 4-byte floating-point. |
|
Double |
IEEE 8-byte floating-point. |
|
Boolean |
Can hold true of false value. |
|
String |
Sequence of characters. |
|
Date |
Unix timestamp. |
|
Blob |
Binary large object (Dashboard projects only). |
|
Stream |
Stream of data (Dashboard projects only). |
|
Any |
Can hold any data type. |
P8.2.2. Structures
Structure types are defined in Variables panel in Structs section. Struct type variable stores multiple data values each accessed by its member name. Each member is defined by its name and type.
Structures can only be used in projects that have EEZ Flow enabled.
P8.2.3. Enums
Enums types are defined in Variables panel in Enums section. Enum type variable stores integer data value, but can contain only restricted set of values. Each enum member is defined by its name and integer value.
P8.2.4. Objects
Object variables, similar to structs, can hold multiple values, each accessed by member names. The member names depends of the type of Object variable. Example of object variables: Instrument connection or PostgreSQL connection. Object variables are described in more detail in Chapter XX.
Object variables can only be used in Dashboard projects.
P8.2.5. Arrays
Array variable stores multiple data values.
P8.2.6. Expressions
An expression contains instructions on how to evaluate a data value during Flow execution. An expression is defined in code similar to JavaScript or other C-like languages.
|
Expression element |
Description / Example |
|
Literal value |
Example: 42, "Hello", true |
|
Variable names |
Example: my_var |
|
Input names |
Retrieves the data stored in data input using the name of that input. Example: input_name |
|
Binary operator |
Example: my_integer_var + 1 |
|
Logical operator |
Example: my_integer_var < 10 |
|
Unary operator |
Example: -my_integer_var
|
|
Ternary operator |
Example: my_integer_var == 1 ? true : false (evaluates to true if my_integer_var is 1, otherwise evaluates to false) |
|
Function calls |
Example: String.length(my_string_var) |
|
Parentheses “()” |
Specifying the order of the evaluation Example: "Counter: " + (a + 1) |
|
Accessor “.” |
Structure type member accessor by using “.” Example: my_struct_var.member1 |
|
Accessor “[]” |
Array element accessor by using “[]” Example: my_array_var[3], my_array_var[index] |
|
Enum value |
Example: MyEnumTypeName.Member1 |
Expression examples:
|
`var[i].member1` |
|
|
|
`var` is array which contains structs, which has member `member1` |
|
|
`i` is integer variable |
|
|
evaluates to `member1` value in the i-th element |
|
|
|
|
`var == State.START || var == State.EMPTY` |
|
|
|
var is of type enum:State, and State enum has two members: START and EMPTY |
|
|
evaluates to True if var contains data that is either State.START or State.EMPTY |
P8.2.7. Literals
|
Type |
Description / Example |
|
Integer |
`42` |
|
Float or double |
`3.14` |
|
String |
`"Hello world!"` |
|
Translated string |
T"text_resource_id" (prefix T is mandatory) |
|
Boolean |
`true` or `false` |
|
JSON |
P8.2.8. Binary Operators
Each binary operators requires two arguments. Binary operator is written between arguments, for example: <arg1> + <arg2>
Addition +
Rules:
- If any of the arguments is a string then result is a string. For example, `voltage +" V"` will evaluate to `"1.5 V"` if data stored in voltage variable is `1.5`
- If any of the arguments is a double then result is a double.
- If one argument is a float and the other is a float or an integer the result will be a float.
- If both arguments are integers then result is an integer.
|
arg1\arg2 |
integer |
float |
double |
string |
boolean |
other_type |
|
integer |
integer |
float |
double |
string |
integer |
err |
|
double |
double |
double |
double |
string |
double |
err |
|
float |
float |
float |
double |
string |
float |
err |
|
string |
string |
string |
string |
string |
string |
err |
|
boolean |
integer |
float |
double |
string |
integer |
err |
|
other_type |
err |
err |
err |
err |
err |
err |
Subtraction –
|
arg1\arg2 |
integer |
float |
double |
boolean |
other_type |
|
integer |
integer |
float |
double |
integer |
err |
|
double |
double |
double |
double |
double |
err |
|
float |
float |
float |
double |
float |
err |
|
boolean |
integer |
float |
double |
integer |
err |
|
other_type |
err |
err |
err |
err |
err |
Multiplication *
|
arg1\arg2 |
integer |
float |
double |
boolean |
other_type |
|
integer |
integer |
float |
double |
integer |
err |
|
double |
double |
double |
double |
double |
err |
|
float |
float |
float |
double |
float |
err |
|
boolean |
integer |
float |
double |
integer |
err |
|
other_type |
err |
err |
err |
err |
err |
Division /
|
arg1\arg2 |
integer |
float |
double |
boolean |
other_type |
|
integer |
integer |
float |
double |
integer |
err |
|
double |
double |
double |
double |
double |
err |
|
float |
float |
float |
double |
float |
err |
|
boolean |
double |
float |
double |
double |
err |
|
other_type |
err |
err |
err |
err |
err |
Remainder %
|
arg1\arg2 |
integer |
float |
double |
boolean |
other_type |
|
integer |
integer |
float |
double |
integer |
err |
|
double |
double |
double |
double |
double |
err |
|
float |
float |
float |
double |
float |
err |
|
boolean |
integer |
float |
double |
integer |
err |
|
other_type |
err |
err |
err |
err |
err |
Left shift <<
|
arg1\arg2 |
integer |
boolean |
other_type |
|
integer |
integer |
integer |
err |
|
boolean |
integer |
integer |
err |
|
other_type |
err |
err |
err |
Right shift >>
|
arg1\arg2 |
integer |
boolean |
other_type |
|
integer |
integer |
integer |
err |
|
boolean |
integer |
integer |
err |
|
other_type |
err |
err |
err |
Binary AND &
|
arg1\arg2 |
integer |
boolean |
other_type |
|
integer |
integer |
integer |
err |
|
boolean |
integer |
integer |
err |
|
other_type |
err |
err |
err |
Binary OR |
|
arg1\arg2 |
integer |
boolean |
other_type |
|
integer |
integer |
integer |
err |
|
boolean |
integer |
integer |
err |
|
other_type |
err |
err |
err |
Binary XOR ^
|
arg1\arg2 |
integer |
boolean |
other_type |
|
integer |
integer |
integer |
err |
|
boolean |
integer |
integer |
err |
|
other_type |
err |
err |
err |
P8.2.9. Logical operators
Logical operators are also binary operators that result in Boolean values.
|
Type |
Description |
|
== |
|
|
!= |
|
|
< |
|
|
> |
|
|
<= |
|
|
>= |
|
|
&& |
|
|
|| |
|
P8.2.10. Unary operators
|
Type |
Description |
|
+ |
|
|
– |
|
|
~ |
|
|
! |
|
P8.2.11. Conditional (ternary) operator
The conditional (ternary) operator is the only operator that takes three operands: a condition followed by a question mark (?), an expression to be executed if the condition is true followed by a colon (:), and finally an expression to be executed if the condition is false.
P8.3. Functions
P8.3.1. System
System.getTick
Retrieves the number of milliseconds that have elapsed since the flow execution was started.
Parameters
None
Return value
Value in milliseconds. Return type is Integer.
P8.3.2. Flow
Flow.index
Index of current element in the List and Grid widget. Check the description of these two widget for the more information.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
index |
Integer |
??? |
Return value
Element index. Return type is Integer.
Flow.isPageActive
If this function is executed inside the page it will return true if that page is currently active page, otherwise it will return false.
Parameters
None
Return value
True if page is active, False if page is not active. Return type is Boolean.
Flow.pageTimelinePosition
If this function is executed inside the page or custom widget it will return the current position at the animation timeline for that page or custom widget.
Parameters
None
Return value
Timeline position. Return type is Boolean.
Flow.makeValue
Creates a new value of type Struct.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
structName |
String |
Structure name. |
|
value |
JSON |
Structure name. |
Return value
Created struct value. Return type is Struct.
Flow.makeArrayValue
Creates a new value of type array.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
value |
JSON |
Array value. |
Return value
Created array value. Return type is Array.
Flow.languages
Retrieves a list of languages defined in multi-language project as array of strings.
Parameters
None
Return value
Array of languages. Return type is Array:string.
Flow.translate
Translate text resource ID, same as T"textResourceID".
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
textResourceID |
String |
Text resource ID. |
Return value
Translated string. Return type is String.
Flow.parseInteger
Parse integer value given as string.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
str |
String |
Input string. |
Return value
Parsed integer value. Return type is Integer.
Flow.parseFloat
Parse float value given as string.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
str |
String |
Input string. |
Return value
Parsed float value. Return type is Float.
Flow.parseDouble
Parse double value give as string.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
str |
String |
Input string. |
Return value
Parsed double value. Return type is Double.
P8.3.3. Date
Date.now
Returns current date.
Parameters
None
Return value
Current datetime. Return type is Now.
Date.toString
Converts given date to string.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
str date |
Date |
Input date. |
Return value
Date string. Return type is String.
Date.toLocaleString
Converts given date to locale string.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
str date |
Date |
Input date. |
Return value
Date string. Return type is String.
Date.fromString
Converts string to date.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
dateStr |
String |
Input string. |
Return value
Date. Return type is Date.
Date.getYear
Get year from date.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
date |
Date |
Input date. |
Return value
Year. Return type is Integer.
Date.getMonth
Get month from date (1 to 12).
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
date |
Date |
Input date. |
Return value
Month. Return type is Integer.
Date.getDay
Get day of the month from date (1 to 31).
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
date |
Date |
Input date. |
Return value
Day. Return type is Integer.
Date.getHours
Get hours from date (0 to 23).
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
date |
Date |
Input date. |
Return value
Hours. Return type is Integer.
Date.getMinutes
Get minutes from date (0 to 59).
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
date |
Date |
Input date. |
Return value
Minutes. Return type is Integer.
Date.getSeconds
Get seconds from date (0 to 59).
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
date |
Date |
Input date. |
Return value
Seconds. Return type is Integer.
Date.getMilliseconds
Get milliseconds from date (0 to 999).
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
date |
Date |
Input date. |
Return value
Milliseconds. Return type is Integer.
Date.make
Make a date from arguments.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
year |
Integer |
Year |
|
month |
Integer |
Month |
|
day |
Integer |
Day |
|
hours |
Integer |
Hours |
|
minutes |
Integer |
Minutes |
|
seconds |
Integer |
Seconds |
|
milliseconds |
Integer |
Milliseconds |
Return value
Constructed date. Return type is Date.
P8.3.4. Math
Math.sin
Returns the sine of a number in radians.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
x |
Integer|Float|Double |
A number representing an angle in radians. |
Return value
The sine of x, between -1 and 1, inclusive. Return type is Float|Double.
Math.cos
Returns the cosine of a number in radians.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
x |
Integer|Float|Double |
A number representing an angle in radians. |
Return value
The cosine of x, between -1 and 1, inclusive. Return type is Float|Double.
Math.pow
Returns the value of a base raised to a power.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
base |
Integer|Float|Double |
Year |
|
exponent |
Integer|Float|Double |
Month |
Return value
A number representing base taken to the power of exponent. Return type is Float|Double.
Math.log
Returns the natural logarithm (base e) of a number.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
x |
Integer|Float|Double |
A number greater than or equal to 0. |
Return value
The natural logarithm (base e) of x. Return type is Float|Double.
Math.log10
Returns the base 10 logarithm of a number.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
x |
Integer|Float|Double |
A number greater than or equal to 0. |
Return value
The base 10 logarithm of x. Return type is Float|Double.
Math.abs
Returns the absolute value of a number.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
x |
Integer|Float|Double |
A number. |
Return value
The absolute value of x. If x is negative (including -0), returns -x. Otherwise, returns x. The result is therefore always a positive number or 0. Return type is Integer|Float|Double.
Math.floor
Always rounds down and returns the largest integer less than or equal to a given number.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
x |
Integer|Float|Double |
A number. |
Return value
The largest integer smaller than or equal to x. It’s the same value as -Math.ceil(-x). Return type is Integer|Float|Double.
Math.ceil
Always rounds up and returns the smaller integer greater than or equal to a given number.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
x |
Integer|Float|Double |
A number. |
Return value
The smallest integer greater than or equal to x. It’s the same value as -Math.floor(-x). Return type is Integer|Float|Double.
Math.round
Returns the value of a number rounded to the nearest integer.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
x |
Integer|Float|Double |
A number. |
Return value
The value of x rounded to the nearest integer. Return type is Integer|Float|Double.
Math.min
Returns the smallest of the numbers given as input parameters.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
value1, …, valueN |
Integer|Float|Double |
Zero or more numbers among which the lowest value will be selected and returned. |
Return value
The smallest of the given numbers. Return type is Integer|Float|Double.
Math.max
Returns the largest of the numbers given as input parameters.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
value1, …, valueN |
Integer|Float|Double |
Zero or more numbers among which the largest value will be selected and returned. |
Return value
The largest of the given numbers. Return type is Integer|Float|Double.
P8.3.5. String
String.length
Returns the length of the string.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
string |
String |
A string. |
Return value
The length of a string. Return type is Integer.
String.substring
Returns the part of the string from the start index up to and excluding the end index, or to the end of the string if no end index is supplied.
Parameters
|
Name |
Optional |
Type |
Description |
|
string |
|
String |
A string. |
|
start |
|
String |
The index of the first character to include in the returned substring. |
|
end |
Yes |
String |
The index of the first character to exclude from the returned substring. |
Return value
A new string containing the specified part of the given string. Return type is String.
String.find
Searches a string and returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified substring.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
string |
String |
A string. |
|
substring |
String |
Substring to search for. |
Return value
The index of the first occurrence of substring found, or -1 if not found. Return type is String.
String.padStart
Pads the current string with another string (multiple times, if needed) until the resulting string reaches the given length.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
string |
String |
A string. |
|
targetLength |
Integer |
The length of the resulting string once the current str has been padded. If the value is less than or equal to str.length, then str is returned as-is. |
|
padString |
String |
The string to pad the current str with. If padString is too long to stay within the targetLength, it will be truncated from the end. |
Return value
A String of the specified targetLength with padString applied from the start. Return type is String.
String.split
Takes a separator parameter and divides a String into an ordered list of substrings by searching for the separator pattern, puts these substrings into an array, and returns the array.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
string |
String |
A string. |
|
separator |
Integer |
The pattern describing where each split should occur. |
Return value
An Array of strings, split at each point where the separator occurs in the given string. Return type is Array:string.
P8.3.6. Array
Array.length
The number of elements in given array.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
array |
Array |
An array. |
Return value
The length of an array. Return type is Integer.
Array.slice
Returns a shallow copy of a portion of an array into a new array object selected from start to end (end not included) where start and end represent the index of items in that array. The original array will not be modified.
Parameters
|
Name |
Optional |
Type |
Description |
|
array |
|
Array |
An array. |
|
start |
|
Integer |
Zero-based index at which to start extraction. |
|
end |
Yes |
Integer |
Zero-based index at which to end extraction. |
Return value
A new array containing the extracted elements. Return type is Array.
Array.allocate
Creates a new array of given size.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
size |
Array |
A size number. |
Return value
A new array. Return type is Array.
Array.append
Takes a separator parameter and divides a String into an ordered list of substrings by searching for the separator pattern, puts these substrings into an array, and returns the array.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
array |
Array |
An array. |
|
value |
Any |
Element value to be appended. |
Return value
A new array with appended element. Return type is Array.
Array.insert
Inserts an element to an existing array at given position and returns a new array. The original array will not be modified.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
array |
Array |
An array. |
|
position |
Integer |
Zero-based index at which new element will be inserted. |
|
value |
Any |
Element value to be inserted. |
Return value
A new array with inserted element. Return type is Array.
Array.remove
Removes from an existing array an element at given position and returns a new array. The original array will not be modified.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
array |
Array |
An array. |
|
position |
Integer |
Zero-based index from which existing element will be inserted. |
Return value
A new array with element removed. Return type is Array.
Array.clone
Deep clone of the array.
Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
array |
Array |
An array. |
Return value
A new array. Return type is Array.
P8.3.7. LVGL
LVGL.MeterTickIndex
See the LVGL Meter Widget description (Chapter XX) for the purpose of this function.
Parameters
None
Return value
Index number. Return type is integer.
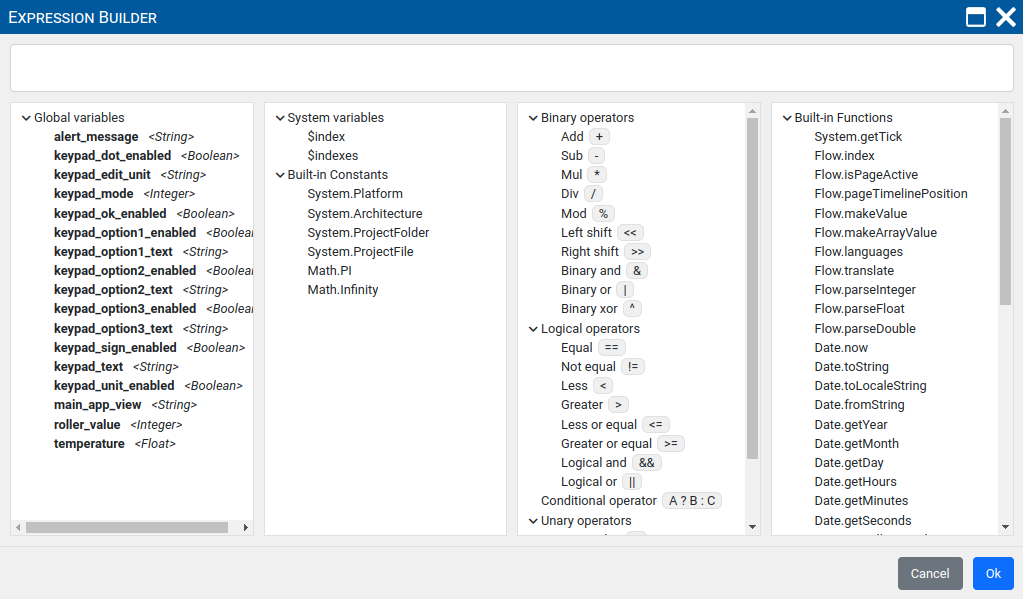
P8.4. Expression Builder
Expressions are supported in both Action and Widget components. Each property of component that can be evaluated from the expression has "…" icon which opens Expression Builder (Fig. 5). Expressions can be entered manually or using the Expression Builder.